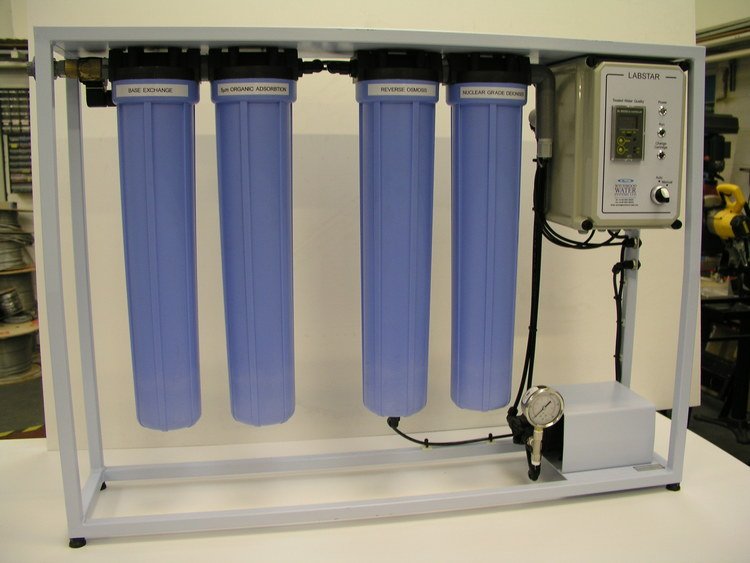
Commercial reverse industrial systems have been gaining popularity in industry because they produce impressive results in water purity without the frequent use of chemicals. Thanks to modern technology, commercial reverse systems are now capable of eliminating more than 99 percent of contaminants from industrial water.
Apart from making desalination possible, reverse osmosis is also a reliable process used to treat any kind of process water, recycle water, and remove most impurities from discharge water used by production industries. Desalination is necessary for industries that use seawater as a coolant, removing minerals such as salt from water to make it pure and safe for process use. Otherwise, the contaminants present in unpurified water might contaminate the products that your company produces, or damage sensitive equipment.
Scientific Explanation Of Reverse Osmosis
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a complicated process. It uses a semi-permeable membrane under great pressure to split clean water from relatively less pure or polluted water. When a semi permeable membrane separates two aqueous solutions that have different concentrations, there will be osmotic pressure, which will force water to move towards the highly concentrated solution. The direction of water flow is reversed by simply applying a greater counter pressure to the more-concentrated solution. As long as the counter pressure is enough to beat the osmotic pressure, there will be a change in the direction of the flow of water.
In the RO membrane, water molecules usually form big hydrogen bonds that can fit well into the osmotic membrane matrix. With enough pressure, it becomes very easy to push such water molecules through. Almost all organic substances that have molecular weight of more than 100 are easily sieved out. Such organic substances include pyrogens, oils and contaminants such as viruses and bacteria.
On the contrary, a mechanism that is related to a valence of an ion will reject any salt ion. Dielectric interactions repel all ions. In fact, the higher the charges, the more the ion is repelled away from the surface of the membrane.
The Reverse Osmosis Membrane
Most manufacturers of industrial reverse osmosis membranes make them from polyamide, polysulfonate and cellulose acetate. The membrane comprises a support layer that measures approximately 100 microns in width and a skin that measures approximately 0.25 microns. Usually, the skin acts as an active barrier to the impurities. It allows only the pure water to pass through. So, the skin ensures that the product water is free from any dissolved substances.
Reverse osmosis produces almost the same volume of water as the total amount of dissolved solids found in any feed water. Let us assume there is 200 ppm solids dissolved in it. In this case, product water can have up to 30 ppm, which represents 90 percent rejection ratio.
Hyper-Filtration
The reverse osmosis plant applies the principle of hyper-filtration, making it one of the most reliable methods for treating industrial water. It eliminates almost all contaminants present in water to make it safe for industrial and commercial applications.
Whenever you need to buy a new commercial reverse osmosis system, simply contact Wychwood Water. We provide systems to purify process water used for industrial and manufacturing across the United Kingdom. We also offer a range of maintenance and repair services.
Find out more about the benefits of reverse osmosis in our Guide To Industrial Reverse Osmosis Systems, which can be downloaded by clicking here.








 We are a specialist independent company involved in water purification and water treatment technologies
We are a specialist independent company involved in water purification and water treatment technologies